O-rings are elastomeric seals typically found in commercial and industrial fluid systems. When compressed between two solid parts, O-rings create a durable, moisture-resistant seal that locks pressurized gas and water inside the system.
Different industries and applications require a wide variety of O-rings. They can be made of different materials, sizes, and in varying shapes. The operating temperatures of O-rings depends on the material makeup, but many are designed to resist tightening or cracking in temperature extremes. PTFE O-rings, for example, can handle a wide temperature range, while silicone and EPDM O-rings function well at low temperatures. O-rings are typically categorized by their material.
Allied Metrics specializes in creating O-rings with a wide selection of plastics and rubber.

O-Ring Types: A Basic Overview
Different types of O-rings fit different industrial, commercial, and consumer uses. Not only do O-rings have to be the right material to withstand the conditions within the operational environment, but they must be the correct size lest the seal develop gaps or weak points. There are also distinct types of O-rings, such as static axial seals, O-rings with reciprocating dynamics, and rotary O-rings.
O-Ring Size
The size of an O-ring can be determined by measuring the diameters and the width of the cross-section. The measurement you will need to include are the internal diameter (ID), outside diameter (OD), and the cross-section width (CS). You can then determine the size of your O-ring using the following equation:
- 2(CS) + ID = OD
O-rings with a smaller cross-section will resist decompression and be more affordable to manufacture and purchase. O-rings with a larger cross-section significantly increase leak protection capabilities. It’s just as important to choose the right size as it is to pick the right material. O-rings come in a wide variety of sizes, including:
- Sizes with metric measurements
- Standard and micro-sizes
- Custom sizes. Allied Metric can create custom O-rings with precision molding and other manufacturing processes to fabricate perfect seals.
O-Ring Operating Temperatures and Applications
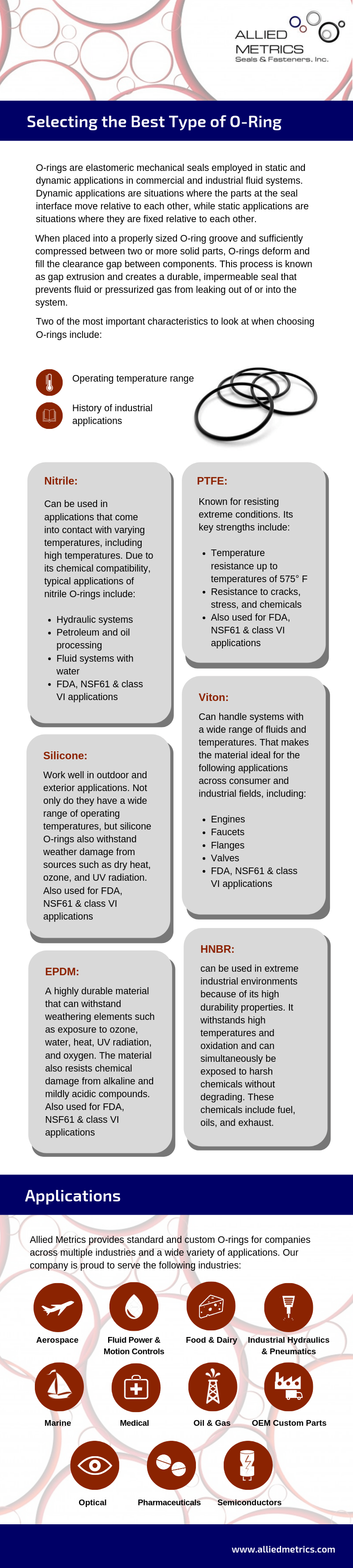
Two of the most important characteristics to look at when choosing O-rings include:
- Operating temperature range
- History of industrial applications
Some materials are used throughout general applications, while more extreme applications tend to default to certain materials with time-tested characteristics. Four of the hardiest specialty O-ring materials are PTFE, Viton, silicone, and nitrile.
Types of O-Rings
Most O-rings are considered static axial seals—they create a tight seal between two parts that don’t move in relation to each other and can be made from materials with lower abrasion and tearing resistance.
Dynamic O-rings, however, hold a seal between moving parts. Not only do these O-rings need to be made from more resilient materials, but they also need more frequent maintenance and lubrication. Dynamic O-rings are classified based on the type of motion they need to withstand, such as reciprocating dynamics or rotary motion.
O-Ring Materials
Once you’ve determined whether you need a dynamic or static O-ring, you’ll need to select the appropriate O-ring material.
PTFE O-Rings
One of PTFE’s most unique characteristics is its resilience to heat and cold damage. The material can stay chemically inert and resistant to abrasion at temperatures ranging from -73° C to 260° C. However, the material is rigid and can be difficult to apply to dynamic or moving parts.
PTFE is known for its viability in extreme conditions. Its key strengths include:
- Temperature resistance up to temperatures of 575° F
- Resistance to cracks, stress, and chemicals
- Suitability for high-pressure applications
PTFE O-rings are commonly found in applications such as automotive steering, chemical processing gaskets, chemical storage, and paint guns.
Silicone O-Rings
Silicone O-rings are important components in outdoor and plumbing systems. The material can handle a wide temperature range between -84–232° C, and resists damage from water, acids, ozone, UV radiation, and heat. Pure silicone O-rings cannot withstand much in the way of wear, tearing, and other physical damage, so it’s best suited to static applications.
Common industries that rely on silicone O-rings include:
- Life sciences
- Medical
- Pharmaceutical
- Food and beverage
- Drinking water
- Semiconductor
Nitrile O-Rings (Buna-N or Acrylonitrile Butadiene Rubber O-Rings)
Nitrile is a resilient elastomer used in a wide variety of industries, such as aerospace and heavy duty equipment. Nitrile can be compounded and processed into several different forms. The material has a strong operational temperature range from -50° C to 120° C, and hydrogenated nitrile can withstand temperatures up to 150° C. However, it is vulnerable to higher temperatures and chemicals such as brake fluid and halogenated hydrocarbons.
Buna is for sturdy, general-purpose O-rings. Buna-N is a nitrile-based synthetic product that has excellent abrasion and tear resistance and withstands exposure to some solvents. Its resistance to weather and ozone damage is significant but can be improved with the addition of other compounds. While Buna O-rings are more cost-effective than fluoroelastomers, they are vulnerable to high temperatures above 149° C.
Nitrile can be used in applications that come into contact with varying temperatures, including high temperatures. Kalrez O-rings, in particular, can operate in temperatures as high as 327° C. Due to its chemical compatibility, typical applications of nitrile O-rings include:
- Hydraulic systems
- Petroleum and oil processing
- Fluid systems with water
- Automotive fuel/oil seals
- Military applications
HNBR O-Rings
Hydrogenated Nitrile Butadiene Rubber (HNBR) O-Rings can be used in extreme industrial environments because of its high durability properties. It withstands high temperatures and oxidation and can simultaneously be exposed to harsh chemicals without degrading. These chemicals include fuel, oils, and exhaust.
Viton O-Rings
Viton O-rings—an alternative to nitrile—provide a reliable seal at high temperatures up to 205° C, or higher for brief intervals. It’s also more resistant to petroleum, acid, and silicone-based fluids than most other materials, and can often be found in oil processing facilities. Viton also features good general wear resistance.
Since Viton can handle systems with a wide range of fluids and temperatures, it is ideal for a wide range of applications, such as:
- Chemical processing
- Automotive fuel systems
- Aerospace
- Oil and gas
EPDM O-Rings
Ethylene propylene diene terpolymer (EPDM) is a highly durable material that can withstand exposure to common weather elements such as ozone, water, steam, heat, UV radiation, and oxygen. The material also resists chemical damage from alkaline and mildly acidic compounds. Common uses for EPDM O-rings may include:
- Pharmaceutical-grade seals
- Medical-grade seals
- Food-grade/FDA-compliant seals
Neoprene O-Rings
Neoprene O-rings are particularly resistant to weather damage, including elements such as UV radiation, ozone exposure, and oxygen that may cause oxidation in other materials. It has a wide operational temperature range of -35–250° F and is resistant to flex cracking and permeation. Neoprene features high resistance to refrigerants and some oils, lubricants, and acids.
Neoprene O-rings are ideal for a narrow range of applications, such as air conditioning and refrigerant systems.
Polyurethane O-Rings
Polyurethane withstands extended contact with CO2, is physically tough, and features good extrusion and abrasion resistances. However, it is vulnerable to heat damage and can only tolerate environments that don’t exceed 100° C. Common applications for Polyurethane O-rings include:
- Valves
- Cylinders
- Pneumatic systems
- Hydraulic fittings
- Firearms
- Fluid transfer systems
Rubber O-Rings
Rubber encompasses a broad category of different materials. This includes fluorocarbon rubber, nitrile, and general-purpose rubber, among others. Rubber is commonly used in less-demanding environments because of its general reliability and low production costs.
X-Rings: An Alternative to O-Rings
When comparing O-Wings vs. X-rings, X-rings have twice the surface area of O-rings and provide a double-sealing action that requires less force and results in fewer leaks. The cross-section of the ring looks like an X, and the edges compress together to provide the double seal.
Benefits of using X-rings include:
- Deeper grooves and more lips for greater sealing capacity
- Lower demand for diametrical squeeze
- Greater resistance to spiral failures in the event of damage
X-rings can be produced with materials that have an operating temperature range of -30° C to 121° C and a hardness of 45-90 on the International Rubber Hardness Degrees scale.
Industries Served
Allied Metrics provides standard and custom O-rings for companies across multiple industries and a wide variety of applications. Our company is proud to serve the following industries:
- Aerospace
- Fluid Power and Motion Controls
- Food and Dairy
- Industrial Hydraulics & Pneumatics
- Marine
- Medical
- Oil & Gas
- OEM Custom Parts
- Optical
- Pharmaceuticals
- Semiconductors
Allied Metrics is a major distributor and manufacturer of affordable seals and related products. For more information about our expansive range of O-rings and other sealing solutions, please contact us.